
The revised methodology is based on the idea that the level of mitigation effort corresponds to the relative position of an emissions pathway in a set of pathways. The methodology was revised in October 2022 in order to incorporate the latest science into this key step. The CAT uses a range of emissions pathways from the IPCC AR6 scenario database to extend the short-term CAT analysis pathways out to 2100. If a major deviation from the BAU scenario described above is found, an adjustment will be applied.
However, we continue to monitor the overall coverage and level of ambition for non-CAT countries. The Climate Action Tracker does not have sufficient resources to individually assess all NDCs. Therefore, we do not assume any deviation from BAU for these countries in the various CAT scenarios as the impact on global emissions and temperatures is expected to be small. Any reduction from BAU for the non-CAT countries would only be a fraction of this amount which is small compared with total emissions. The baseline construction is described in greater detail on the PRIMAP website.Īlthough the CAT doesn’t directly assess many countries that have submitted an NDC, these countries together are only responsible for a small share of emissions in 2030 under our BAU scenario. The BAU pathways used in this analysis are from the PRIMAP4 baseline. For countries that are not individually assessed, we either use NDC quantification by the mitiQ tool (Günther et al, 2021) or assume that the emissions of these countries will follow a ‘business-as-usual’ (BAU) pathway. Each of these steps is described below.Ĭountries assessed by the Climate Action Tracker were responsible for 81% of global emissions in 2010 (excluding LULUCF).
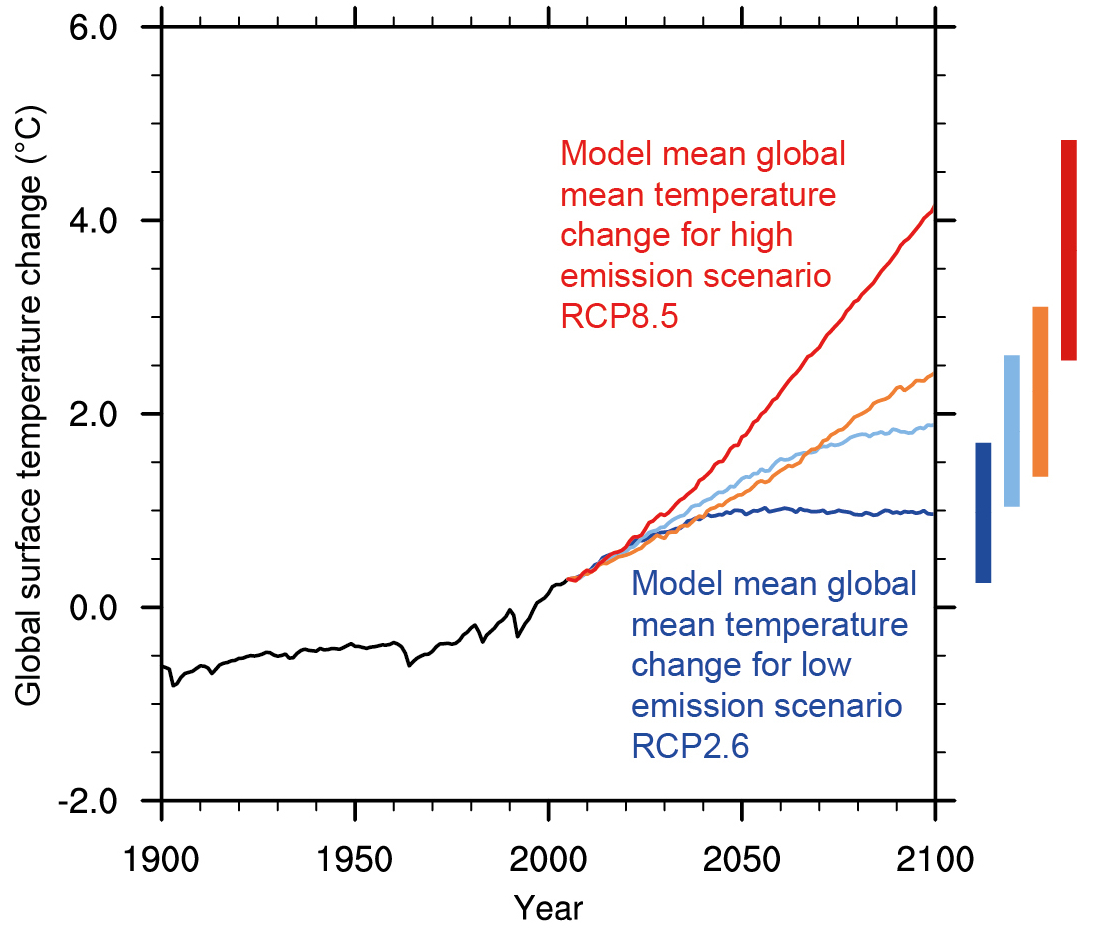
the global mean warming in 2100 and corresponding temperature exceedance likelihoods over the 21st century. These distributions are used for deriving the central median estimate of e.g. MAGICC7 is run multiple times in order to obtain a probability distribution of outcomes such as global mean temperature, CO 2 concentration, and total greenhouse gas concentration. The MAGICC emulations reflect the complex model response ranges for the assessed scenarios in the calibration datasets, in particular the Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs). This global pathway is then used as input to a reduced-complexity carbon-cycle / climate model ( MAGICC7) which is calibrated against data from complex general circulation models (GCMs), including climate sensitivity and carbon cycle information. To assess the climatic impact of the targets put forward by countries, we first construct a global emissions pathway to 2100.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
